We interact with air every breath we take. We inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Many complex cycles occur in tandem within our atmosphere, including the water and carbon cycles. The air consists of various components – mainly oxygen (O), carbon dioxide (CO₂) and dinitrogen gas (N₂) with small amounts of water vapor and gas components that are encompassed within these complex cycles. 30 15 Changes in the atmosphere are based on weather conditions and chemical levels that fluctuate alongside the aforementioned cycles.
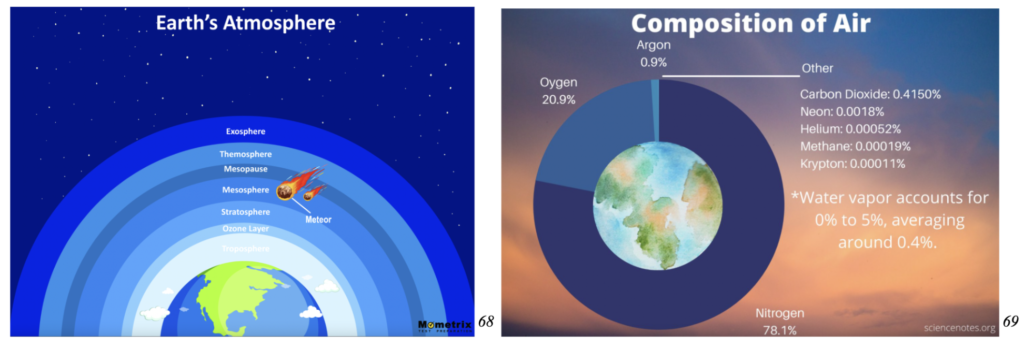
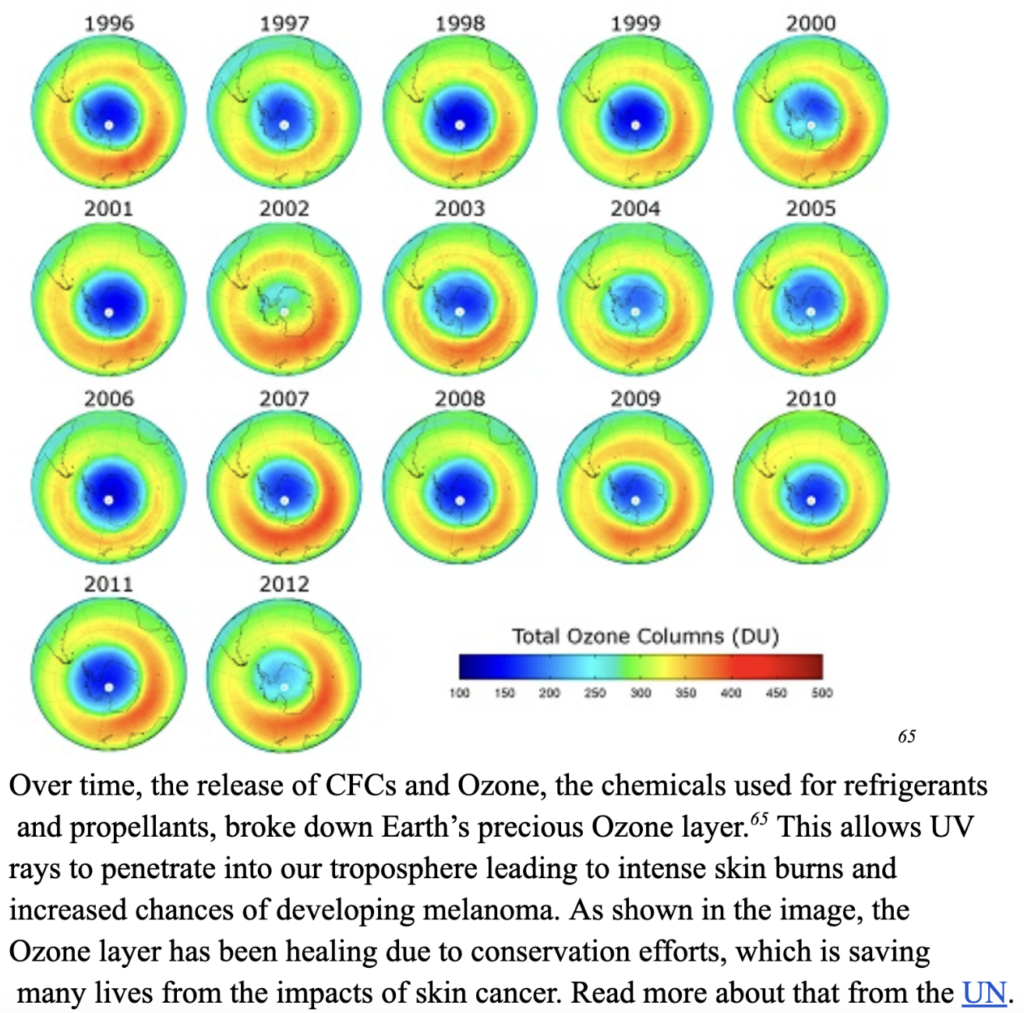
For example, as warm air rises and cold air enters, wind is created which moves around particles. Reactive chemical levels can also change the atmosphere which can explain the possibility of recent ozone depletion and rebuilding-forming chemicals (nitrous oxides). 36
An overview of Air Quality and Associated Climatic Issues
What is Poor Air Quality:
Classified as dust, fumes, gas, mist, odor, smoke or vapor.
The EPA Criteria Pollutants include:
- Carbon monoxide
- Lead
- Nitrogen oxides
- Ground-level ozone
- Particulate matter (PM)
Learn more about the criteria pollutants and general air pollution on the EPA’s website. Link to: CDC Air Pollutants 9
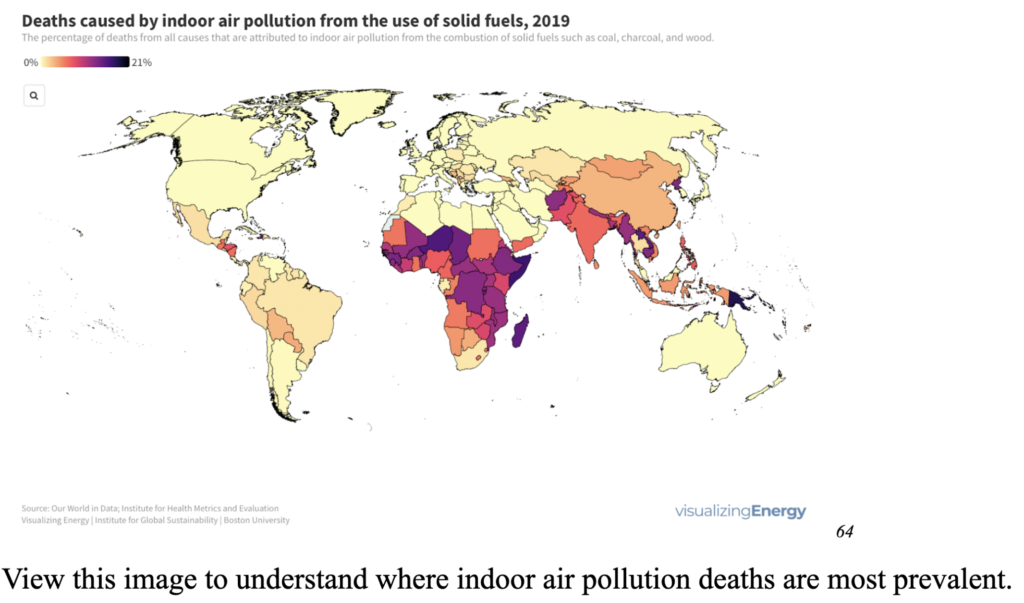
Natural sources of air pollution include forests and wildlands fires, dust storms, sea salt spray/ ocean processes, and volcanic activity



Most significant toxins that impact human health:
- Particulate matter (PM) are small particles that can harm and or cut deep into your lungs, enter your bloodstream, and travel to essential organs. This can severely damage tissues and cells.
- Components: Mainly sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
- Source: Emitted from big industry, automobiles, indoor and outdoor fires
- Most common PM is PM10 (10 micrometers or less) and PM2.5 (2.5 micrometers or less.
To put that into perspective, one singular stand of human hair is approximately 100 micrometers. 42 60
- Carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Most susceptible groups: children, elderly and pregnant women. Certain genetic conditions, sociodemographic factors, and nutritional decisions contribute to a person’s susceptibility to air pollution. BIPOC and poor minority communities are disproportionately affected by air pollution. 60
- Sources: Waste-to-energy plants, power plants, burning of fossil fuels, Vehicle emissions
- Acid (Nitrous Oxide and sulfur dioxide): Found in a liquid (acid rain) or gas
- Source: Commonly emitted through fossil fuel combustion 37
- Impact:
- Alters the soil chemistry, dissolve nutrients, and corrodes bridges and weathers stone buildings
- Can exacerbate existing health issues.
- Most present in urban areas. Impacts acidity of ocean water, soil, etc. jeopardizing essential resources
- Lead & Metals
- Sources: Metal smelting, waste incinerators, Battery manufacturing, factory operation, Old lead-based paint, pipes and other household products 51
- Impact:
- Long-term human health issues: increased risk of…
- High blood pressure, cardiovascular problems & kidney damage
- Lead can accumulate and reach your brain, liver, kidney and bones, causing many health issues
- Most susceptible groups:
- Children: Can create brain and central nervous system damage, cause coma, convulsions and even death
- Pregnant women: Can lead to a miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth and low birth weight 61
- Long-term human health issues: increased risk of…
EXPOSURE TO ALL OF THESE HARMFUL POLLUTANTS IS PREVENTABLE
General Impact of Poor Air Quality
- Human and animal health implications (please note, these symptom include many pollutants)
- Short-term symptoms: throat irritation, congestion, difficulty breathing, headaches, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and chest pain or confusion.
Long Term Symptoms: inflammation (general or airway), oxidative stress, immunosuppression, and mutagenicity in cells throughout our body impacting the lungs, heart, brain among other organs stroke, pneumonia. 59
Diseases associated air pollution exposure:
- Respiratory issues such as asthma, ischaemic heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer 60
View air quality conditions around the world with Breezometer
Air Pollution and its Link to Climate Change and Global Warming
Greenhouse gasses are air pollutants, defined as any gas that traps heat in Earth’s atmosphere, amplifying the natural greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is a natural condition which enables Earth to be a habitable temperature and climate.

In our industrial world, greenhouse gasses are being emitted at a rate that results in a net increase in global temperatures. This changes Earth’s climate, leading to cascading environmental effects.28
Key greenhouse gasses (GHG) contribute to climate change; some examples are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, ozone (O₃ = NOx and VOC) and other synthetic chemicals. Each GHG lingers within the atmosphere for certain periods of time, each with a different chemical lifetime and ability to absorb and reflect heat. A compound like ozone is good in the atmosphere, however, becomes toxic in the troposphere of the earth.31
Climate Change VS Global Warming
Climate Change – The change in the frequency, intensity and variability of our climate and weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and other factors.
Global Warming – The net warming of global temperatures due to an increased presence of greenhouse gasses in our atmosphere.

Miami’s Particular Challenges
Pollution Created by Tourism, Transportation & Big Business practices:
Miami is one of the most congested cities in the world, ranking 5th for worst traffic nationally and 9th worldwide by INRIX in 2023. Florida state reports show that Miami’s traffic increased 30% from 2021 to 2022. 18 INRIX attributed the congestion to new residents moving to South Florida and the vibrant nightlife and restaurant scene which draws people in. 44

Driving in the City of Miami has been described as “complete madness.” It experiences a large influx of tourists visiting from within state, national and international boundaries.
The City of Miami welcomed…10
- 33.1 million visitors from the state of Florida (April-June 2023)
- 1.9 million tourists from overseas
- 846,000 of those visitors originating from Canada (April-June 2023)
This totaled to 70.8 million visitors enjoying Miami during that time frame.10
- +1.3% during the first half of 2022 & +4.5% increase above pre-pandemic levels in 2019 from overall tourism
- International tourism grew +4.4%
- In state resident visitation +25%
Within the hospitality sector, the Greater Miami Convention & Visitors Bureau sales team calculated a +56% increase in confirmed bookings in 2023 which was up by 48% in 2022.10
If you consider the growth and development of Miami’s population, with decreasing amounts of permanent residents and increasing number of temporary tourists, it becomes clear that pollution problems will likely to get worse.4
According to a 2013 Miami air quality report, most of Miami-Dade’s air pollution is attributed to motor vehicle emissions. Even a decade ago in 2013, there was more vehicle growth than population growth in Miami.1
While there is no specific information on Miami’s tourist emissions, globally tourists generate an estimated 11% of GHG emissions. This number is anticipated to double by 2050. In that circumstance our planet will have warmed 2.7F above pre-industrial times. By the end of the century, the figure looks to be 3.6F.
Read to learn more about Miami’s Air Quality at The Miami Herald.
Each year the American Lung Association creates a “State of the Air” report which highlights air quality in areas around the country.
- Overall from 2022-2023, Miami experienced fewer days with high ozone contamination as the ranking shifted from 100th in 2022 to 111th in 2023.
- Miami-Dade County received a “B” grade for ozone pollution.
- Generally, the county experienced worsened particulate pollution leading to the county to be tied at 83rd worst for short-term particle pollution.
While some national legislation, namely the Clean Air Act, is improving our Earth’s ozone pollution, Senior Director of Advocacy for Florida’s chapter of the American Lung Association, Ashley Lyerly, says there is a lot more to improve as many are left at highest risk for pollution related symptoms.3

Contrails from Miami International Airport
Miami International Airport (MIA) is one of the fastest growing airports in the United States. It has been ranked the second busiest airport in the United States this past year and experienced record-breaking traveler and investment rankings.14
This year MIA welcomed 52 million people through their gates and this number is anticipated to rise to 77 million passengers by 2040. 8 The airport is undergoing a historic $7 billion investment in capital infrastructure and $1.7 billion in maintenance. Part of their maintenance projects are to mitigate impacts of erosion and decrease the buildings energy consumption as monthly electricity costs more than $2 million.16
Shockingly Miami International Airport does not mention contrail pollutants at all on their websites.14

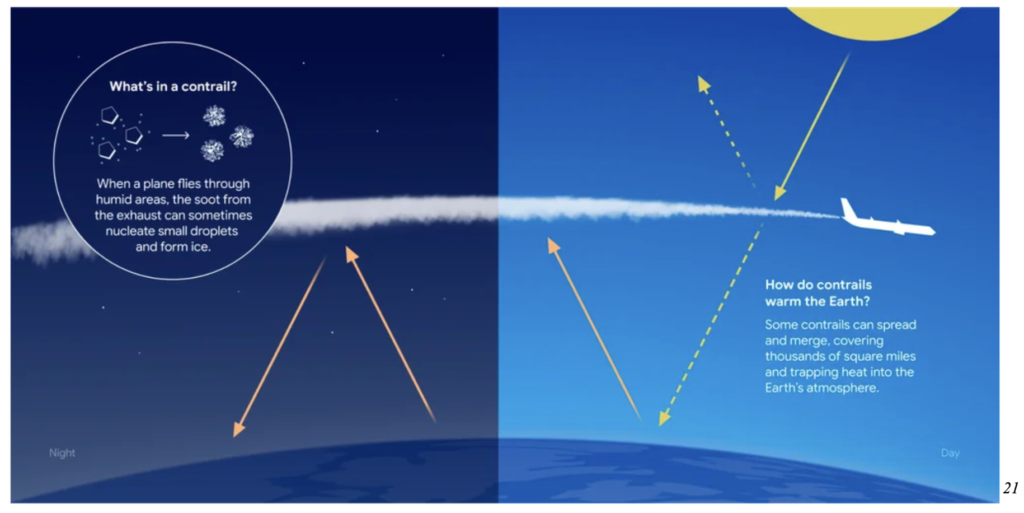
Contrails are the straight lines you see in the sky following a plane. Although contrails may look like normal clouds, they are actually human made clouds that form in the air as moisture condenses and freezes around carbon particles and exhaust in jet engines. While clouds and contrails form similarly, clouds latch onto dust particles with contrails attached to air pollution, spreading carbon around to almost every inch of the world.
Normal clouds are an essential aspect of Earth’s climate systems as they reflect the sun and shade our ground; however, they also trap heat and humidity. Contrails have the same effect, which doubles their impact on global warming. 33 47
According to NASA, most commercial flights fly at 26,000 feet or higher, where temperatures support the formation of large volumes of condensed vapor that instantly freeze. This creates ideal conditions for visible or invisible contrail clouds to form. 47
On average, a single passenger flying to and from London to New York, an 8 hour and 15 minute flight, will generate about 986 kg of CO2. That is a large amount of associated emissions considering that there are 56 countries where the average citizen is responsible for less CO2 in a year. 39 Generally, Aviation accounts for 3.5 percent of human-caused global warming.46
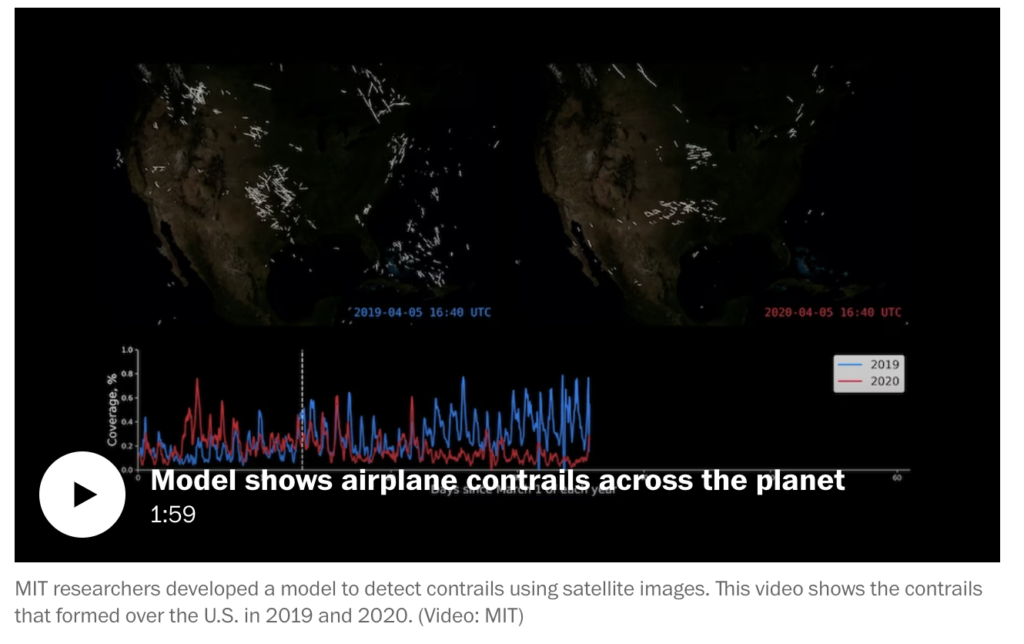
Click on the image to and scroll the video to view contrails across the canvas.
View this The Guardian article to determine your next flight’s emissions.
Insert chart of impacts of contrails: 24
- Global net warming effect (Global Warming)
- Change in wind, weather and jet stream patterns
- Alter the components of
- Ozone layer depletion 24
View this article from the Washington Post that shows a solution that the airlines such as American, Delta and KLM are implementing. While reducing concentrated contrails has an impact on air quality locally, generally, contrails remain a global air quality challenge.
A Shared Sky
We all share one sky and one atmosphere. This interconnection means the pollution on one side of the globe reaches another. Just a mere 4 hour drive away is NASA’s John F. Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
Rocket Launches happen frequently, spewing black carbon and kerosene into the atmosphere which may further damage the protective ozone layer our global community has worked so hard to protect. Not only would further ozone depletion become a health and safety hazard but it would also contribute to already changing atmospheric circulation patterns.
NASA is moving towards powering rockets with hydrocarbons, but there are associated problems with those as well. 24
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) research team formulated a climate model that approximated that 10,000 metric tons of soot (a black powdery atmospheric carbon) pollution has been injected into the upper level of the atmosphere over the northern hemisphere every year for 50 years. That means that an estimated 1,000 tons of rocket soot is emitted annually. 24
These emissions are not going away, in fact, spaceflight demands are expected to grow due to the privatization of space exploration by companies such as Boeing, SpaceX, Blue Origin, and possibly more looking to bring civilians into space.24
View full NASA launch schedule here.
Based on the 2019-2021 Community Health Needs Assessment of South Florida, conducted by the University of Miami, a major concern for citizens are long-term health issues such as diabetes and asthma, especially in children. There is acknowledgement of the factors contributing exacerbated conditions: Disparities in access to health insurance, social and economic factors which are amplified by the aforementioned housing affordability crisis and of course, air and water pollution. Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease was the number 4 leading cause of deaths in Miami-Dade County in 2017 – this totaled to 1,074 deaths.57
Other Resources:
- View MIA’s green initiatives on their website Miami University’s college of engineering has an aerosol and air quality research lab which focuses on aerosols. View the lab’s publications on Aerosols research
- Illustrated through this resource created by NASA, see the emission trends pre and post the start of the COVID-19 pandemic – embed link https://airquality.gsfc.nasa.gov/slider/pandemic-and-after-florida-2015-2019-versus-2020
- See Miami-Dade’s active air quality report – embed https://www.iqair.com/us/usa/florida/miami
- Learn about air quality and air quality alerts at the Miami Valley regional Planning Commitee’s website
Global Warming:
Global warming is defined as the overall net warming of our Earth’s temperatures due to an increased presence of greenhouse gasses in our atmosphere. This process is scientifically proven to be human accelerated. Learn more specifics through NASA’s website.
As mentioned in the introduction, Florida is a climate denying state. This means that many citizens and people in power reject the claim that climate change and its subsequent effects are driven by human activity (despite the sufficient scientific evidence).
Climate change has a cascading amount of negative impacts on our physical and natural environments. One of the most prevalent and tangible changes is the increased frequency of extreme weather events. More specifically for the state of Florida, extreme heat occurrences.13
Extreme heat is defined as a period of time where high heat and humidity contribute to temperatures above 90 degrees for at least 2-3 days. 13 Extreme heat is felt more in cities due to their urban development patterns, this phenomenon is known as the ‘urban heat island’ effect. This effect is experienced when cities replace natural surfaces with impermeable and or dark pavement, buildings, and other surfaces. The characteristics of these surfaces absorb and retain heat as opposed to reflect it. Learn more about the ‘urban heat island’ effect on the EPA’s website. 58 22
I spoke with Benjamin Delin, a former Palm Beach County resident/ Resilience and Sustainability Analyst for Palm Beach County, who mentioned the lack of urban planning infrastructure in Southern Florida. Certain city developers are creating tall black buildings which radiate warm air into its surroundings, similar to the building pictured below. The color black absorbs heat. This can lead to black buildings demanding more energy use due to increased air conditioner needs or can impact passerbyers who experience significantly warmer temperatures as they walk by (B. Delin, personal communication, Feb 10, 2023). This may not seem like a significant difference, however, this can be the difference between 105 degreess fahrenheit and 110 degrees fahrenheit – the threshold for increased sufficient chances of heat exhaustion and heat stroke.23
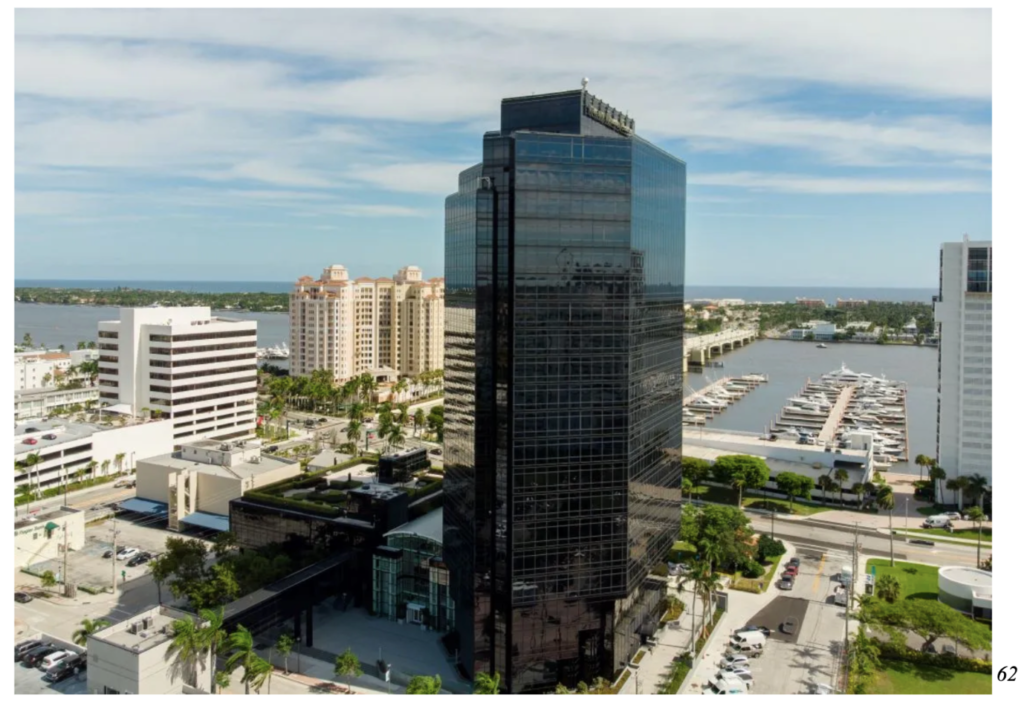

Impacts of Urban Heat Island Effect
The urban heat island effect increases energy costs (e.g., for air conditioning), air pollution levels, and heat-related illness and mortality rates, especially within children. Certain services reflect and conduct heat better than others. In talking to Benjamin Delin, he identified a prevalent trend – the popularity of artificial turf installation within counties, cities and homes in South Florida. He mentioned the transition of major public parks to artificial turf due to the low maintenance. Turf fields do not require much upkeep and cut down on county water usage, though they decrease biodiversity, permeable surfaces and lead to the pollution of waterways and even human bodies. Studies prove that turf contains chemicals which can lead to cancer, especially in young children.53
As I digress, the most relevant danger of turf is its ability to radiate heat. Around the world, too many people are dying directly or indirectly due to heat. Just in the state of Florida, from 2010 to 2020, the state saw 215 deaths that were directly related to heat. Even more people struggled from extreme heat illness. 22
This past summer, Florida experienced record-breaking high temperatures. Emergency Medical Service calls are increasing in summer months due to heat related occurrence and Miami-Dade county is estimated to on average have 34 heat related deaths each year attributed to conditions such as heat stress and stroke.22
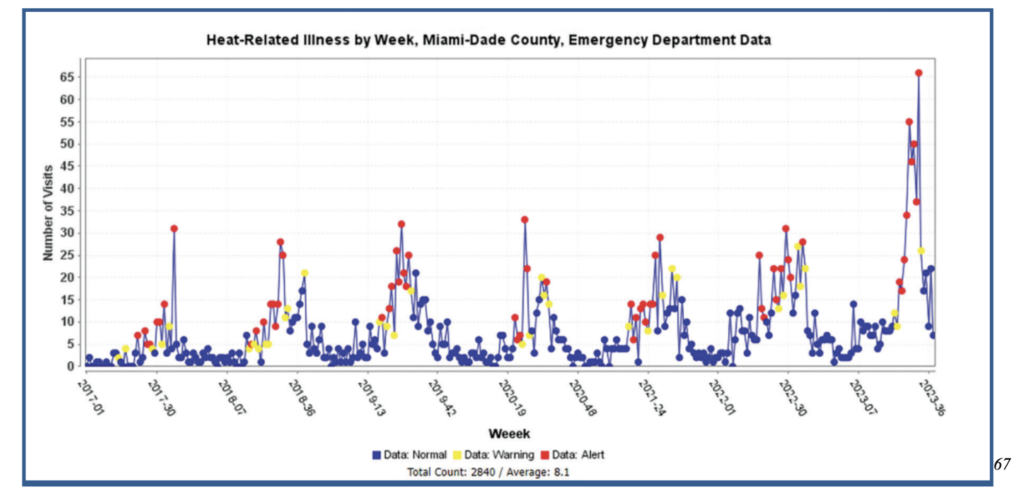
Delin shared with me jarring statistics: from 2010-2020 there were 14 heat related deaths of children ages 0-14. Out of those 14 children, 7 of those were ages 1-5. These deaths were directly results of children playing on hot turf sports fields in public and private parks (B. Delin, personal communication, Feb 10, 2023). This is a perfect example of a solution to one problem that saved money and resources in the short-term but has had significant externalities in the long-term.
View Yelp’s best turf field here. Notice how many of these parks are managed by the city and focus on children’s outdoor sports activities.
Further items that amplify the heat…
- Lack of vegetation such as trees of grass that have net cooling effects. Trees also provide natural shade
- “A single tree absorbs as much as 600,000 Btu of solar radiation every day” 45
- Prevalence of tall buildings which block wind
- Existence of asphalt parking areas, streets, etc. nearby
- Lack of proximity to water sources
Read this resource of a South Florida Local explaining the issue. Read more about Miami-Dade’s specific information through their StoryMap.
Light Pollution:
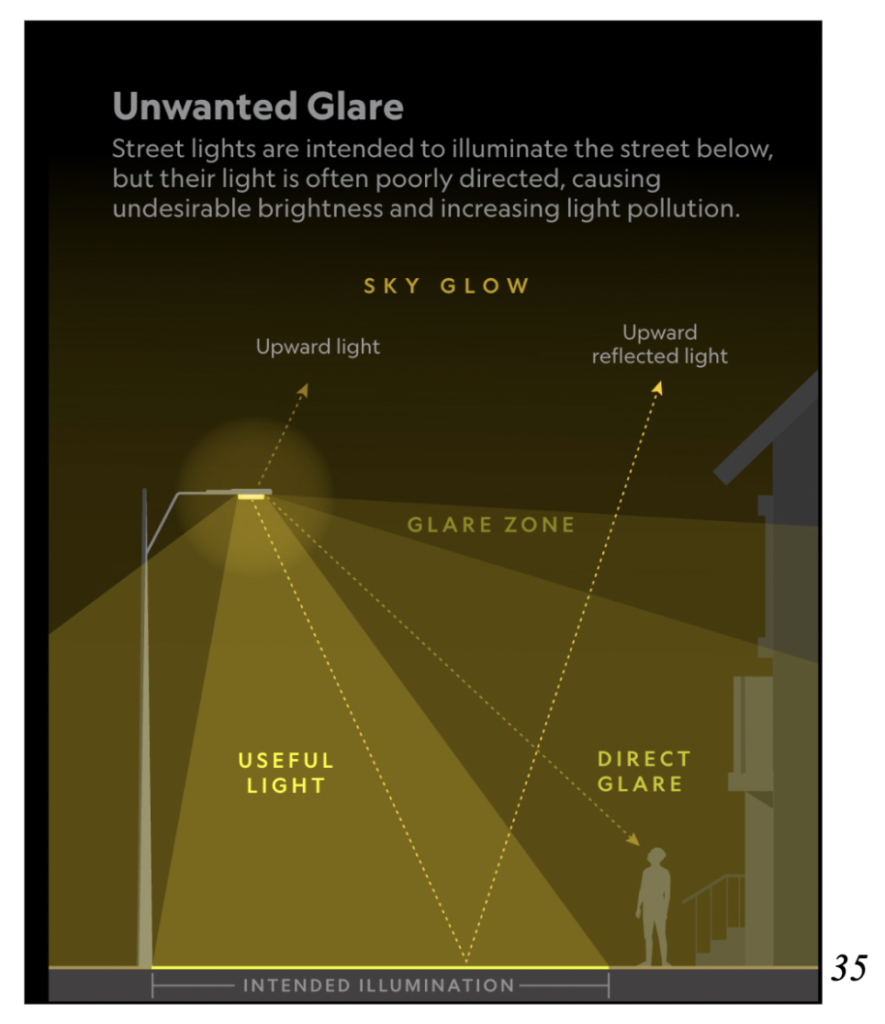
Light pollution is a type of air pollution that typically slips under the radar and out of people’s minds; however it should be talked about more as an approximated 80% of people on Earth have lost their view of the natural night sky due to artificial lighting, according to a 2016 study. 20
Light pollution is characterized by a human-made presence of excessive artificial lighting to an extent in which it can have adverse effects on the quality of our environments. Light pollution is most often non-naturally occurring light. Since Miami is a vibrant city, light use comes along with it – whether it is a drone show, advertising lights or outdoor parties, immense amounts of light are thrown into our night sky.

View visually the level of light pollution in Southern Florida at these locations: https://www.cleardarksky.com/lp/MiamiFLlp.html
https://darksitefinder.com/maps/world.html#6/27.738/-79.752
https://www.lightpollutionmap.info/#google_vignette
Impact of light pollution:
Effects on overall human mood and mental health 35
- Can lead to depression, cancer and a range of sleep disorders because we are altering our circadian and biochemical rhythms.
- Poor sleep can impact our cognition, blood pressure, immune system, metabolism.
- Loss of cultural and personal connection to nighttime skies, a resource our ancestors used to rely on for survival.35 34
Disrupts migratory patterns of bird and photosynthesis 27
- Songbirds fly over Miami at night to migrate along the Atlantic Flyway to achieve cooler, calmer and safer flight. The nocturnal migrants use navigational tools such as magnetic fields and the stars, to keep them on course.
Animals are unable to adapt at a fast enough rates to counter the effects 27
- Leads to endangered species or even species extraction as increased light harms and stresses animals whose life cycles depend on dark
Indirect effects: Contributes CO2 levels as energy generation for unnecessary light is generated by likely fossil fuels.


Relevant Stakeholders:
Pollution from Tourism, Transportation & Big Business practices 52
| Institutions: Greater Miami Convention & Visitors Bureau is in charge of tourism and markets to many potential visitors daily. Any changes in the field and solutions will likely affect them. They also have a large amount of reach, meaning they can support organizations in creating meaningful change regarding this issue. |
| Agencies: Miami-Dade County Government Specific Dept. The following departments should be in collaboration… Department of Cultural Affairs Miami-Dade County Tourist Development Council The City of Miami Beach, located in Miami-Dade County, receives many tourists, hence they have a stake in changes. Seaport. Many of Miami’s tourists come through the seaport or pass through there, they have a great potential to reach many visitors. & the surrounding counties: Broward Palm Beach, Florida Keys and the Glades interior counties |
| Non-Profit Organizations Pelican Harbor Seabird Station, Inc. Transit Alliance Miami & more |
Extreme Heat and the Urban Heat Island Effect 52
| Agencies/ Institution: Miami-Dade County Government Specific Dept. The following departments should be in collaboration When this becomes a more prevalent issues, the Communications and Customer Experience team will likely have to deal with the public to combat concerns Extreme Heat has the potential to put the county in a state of emergency, hence why Emergency Management should be collaborated with. Many EMS services are offered by the Fire Rescue team. A collaboration between EMS and Juvenile Services the Medical Examiner’s office could be powerful. Miami-Dade Police Department Water and Sewage and Parks, Recreation and Open Spaces would provide good perspectives as turf was added to decrease water usage. They could be alternative solutions to the problem that may require bringing back green space. Private EMS Services Miami Dade Ambulance MCT Express Ambulance Services AMR Miami-Dade And possibly more Miami Youth Groups Miami Youth Sports Leagues YMCA of South Florida Other Youth Athletics Programs & the surrounding counties: Broward, Palm Beach, Florida Keys and the Glades interior counties |
| Non-Profit Organizations: The Miami Foundation Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center & more |
Contrails from Aviation 52
| Agencies/ Institution: Residents of Miami Neighboring communities Greater Miami Convention & Visitors Bureau is in charge of tourism and markets to many potential visitors daily. Any changes in the field and solutions will likely affect them. They also have a large amount of reach, meaning they can support organizations in creating meaningful change regarding this issue. Community Action and Human Services Miami-Dade County Government – the following departments should be in collaboration… Aviation (Miami International Airport) Regulatory and Economic Resources as they work with permits Strategic Procurement would bring a good perspective into how to acquire the resources to make meaningful impacts Transportation and Public Works & the surrounding counties: Broward Palm Beach, Florida Keys and the Glades interior counties |
| Non-Profit Organizations: Local environmental foundations: Biscayne Bay Foundation American Lung Association The Sierra Club Miami Group & more |
Solutions:
Miami’s Current Solutions
Much of Miami-Dade County’s approach to mitigate their impact with regards to air pollution stems from the resiliency office that works on climate medication and adaptation. James F. Murley, Chief Resilience Officer, who works on various projects to increase Miami’s ability to withstand their climate challenges.
Based on the department’s home page, there are a variety of types of events and collaborations with community partners to solve issues. 40
In terms of the urban heat island effect, the Department of Resilience has been working on a multifaceted program to prevent heat related illnesses and deaths through public education, policies and partnerships. The department created a 2023 Extreme Heat Summary that crunched important numbers and provided a baseline for further research and new partnerships.
Below are the elements of the initiative:
- 2023 Extreme Heat Summary
- Billboard education
- Public outreach program through raising awareness of health safety training and heat response protocols
- A Miami-Dade County Extreme Heat Action Plan
- Three actionable and measurable items:
- Informing, preparing and protecting citizens through outreach.
- Cooling homes and emergency facilities by improving access to efficient and reliable cooling in homes
- Expanding the presence of trees, vegetation, and water features as well as implementing shade structures and cool surfaces.
- Three actionable and measurable items:
See how a local non-profit, The Miami Foundation is adding to this solution.48
The effectiveness is unclear as it has just been implemented, however the extreme heat action plan is detailed, showing the steps were well thought out. Other states such as New York and California have implemented similar plans with good success.
It is clear that cities are trying to get to the root of the problem, and preventing deaths/citizen harm, but the main root of this problem is climate change. In Florida, it is unclear how effective their policies to decrease it are and how committed the government is as commitment to our environment varies internally. For example, Ron DeSantis, Florida governor, rejected millions in climate funding despite the state’s clear impact attributed to climate change. 41
After researching, it has become clear that nature-based Solutions are great for all of the aforementioned issues in this section. Specifically, further implementing the use of greenery and tree canopies would support both climate and air quality challenges.
Nature-Based Solutions
Plants sequester carbon dioxide and decrease surface temperatures. Research shows that urban forests can lower overall temperatures by an average of 2.9°F in urban areas. 45 Implementing green road and highway infrastructure has immense potential to mitigate the impact of climate change and decrease urban area’s carbon footprint. Highways are never going away. Society has a great opportunity now to create the infrastructure which can support our traffic needs and sequester carbon while having other positive externalities. 47
Miami does have plans to restore trees and urban forests. See those plans here.
Congestion/ Transportation Tax
NYC’s Congestion Tax
New York City recently announced that a congestion tax will be implemented starting late Spring 2024. This tax will impact the Manhattan area, changing passenger vehicles $15, trucks $24-$36 depending on their size, and motorcycles $7.50 for traveling from 60th Street to the southern tip of the Financial District.
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) board approved this policy as it will enable them to fundraise millions of dollars to invest in the city’s aging transit system. It will also decrease GHG emissions and increase the use of public transit, walking, biking, etc. to get around in the city. While I don’t agree exactly with the tax, I do appreciate the idea of incentives being put in place to all stakeholders – locals, business owners, corporations. Policies that mobilize the power of incentives can be characterized precautionary actions that pertain to proactively preventing negative outcomes in the future by addressing them in the present. 49
The motivation behind this new policy is strong, however, the implementation of the incentive needs improvement.
Listed are strong-suites of the policy…49
- Decreases GHG emissions
- Supports local business
- Stimulates local economies by forcing businesses to supply items locally
- Incentivize carpooling, public transit, walking, biking, etc.
- Conserves NYC’s resources
- Decrease car congestions (and air quality)
- Creates a fund to invest in quality infrastructure
Listed are downsides of the policy… 49
- Disadvantages New Jersey commuters
- Will likely overload the NJ and NYC transit systems, even more as the public transportation infrastructure is not developed to the support a higher influx of people
- Will likely lead local inflation to the local economy due to distribution price increases
- Disadvantages Staten Island as it will disincentivize people to travel there via ferry
England’s Car Tax
This kind of legislation likely took inspiration from the Car tax (vehicle excise tax) which was implemented in England that mandated citizens to register their vehicle based on CO2 emissions. This tax increased the purchasing of electric cars, as well as the use of public transportation. The one difference between England and the New York area is that the public transportation infrastructure exists to support a change like that. While New York would like to raise funds to invest in infrastructure, making a drastic shift like they plan to will likely backfire due to the limitations of the policy; however it is so important to acknowledge the effectiveness of the idea. 29
Miami’s Urban Partnership Agreement
Miami works with Fort Lauderdale to manage a lane facility on a section of Interstate 95 (I-95). The area spans 21 miles, running between Interstate 395 (I-395) and Interstate 595 (I-595), two areas known for heavy traffic congestion. 70
Lanes are sectioned into expressways where traffic flow and access are managed with strategies…
- Fixed tolls
- HOV (high-occupancy vehicle) lanes (lanes that encourage ridesharing, this highway featuring HOV 2+ & 3+ people)
- Variable pricing based on demand
The variable tolls can adjust as frequently as every three minutes to adapt to changing traffic conditions to decrease congestion and enable free-flowing traffic. Most tolls are collected through “SunPass” transponders and electronic readers and through video license plate readers. The revenue from the tolls support the operation and maintenance of the Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system. This solution incentivizes use of the BRT system, which is designed for a faster, more efficient commute. This new system creates a better service compared to traditional bus routes, due to dedicated lanes and limited stops.70
The Urban Partnership Agreement is dissimilar to the aforementioned solutions in NYC and England as it take into account demand and incentivizes commuting at off times. This many lead to people taking public transport, carpooling or deceases the GHG emissions from loitering in traffic on their commute. One positive of this solution is that it does not create as inflation, like the NYC tax will likely do. the Urban Partnership Agreement better support the local community and public transport system.
Limitations/Barriers related to these kinds of initiative
- US Government challenges. The government can move slow and be very divided
- Corporate Influence. Corporations have lot of social and monetary power – this can be a strength
- Public transportation, carpools, etc are not always accessible to people
- Just like sustainability
- Air pollutions is a global issue that crosses country boundaries
- Lack of infrastructure: Big policy changes need the proper infrastructure to support it such as social programs, transportation resources, application avenues etc
- Investment/ high prices: There are high cost associated with creating the infrastructure
- Urbanization is a double edged sword. It can have many social and economic advantages however the need to support so many people can get in the way of sustainable development/ implementing solutions
- Climate change continues to surprise us. Changes in weather systems and increases make conditions unpredictable.

View the EPA’s suggestions on how you can reduce your impact on air pollution.
Conclusion
Miami-Dade County overall has shown an awareness of sustainable action and is encompassing some elements identified in my working definition of sustainability such as…
- Serving to meet the social & economic needs of the present and future population through Miami’s sustainable action
- Considering the standard of human well-being to ensure basic human rights are satisfied with Miami’s solutions
Note: That this is one aspect of the city’s sustainability. I will examine it’s sustainability as whole later in the website.
In Miami, it is evident that great policies and solo nonprofit work exists in the area such as those listed above like The Miami Foundation, Miami-Dade County Extreme Heat Action Plan, 2023 Extreme Heat Summary, and Climate Action Plan. Policy alone is not sufficient for change as they do not lay the groundwork to collect meaningful data for governments to leverage in their actions to address problems. Moreover, a one layered solution can only have so much impact. This is why I believe increased multilateral support, in terms of the aforementioned climate challenges, can be transformative. More partnerships with governments and the private sectors between NGOs, who emphasize empowerment, can improve communities on the local and global scale.
Broad list of Assets
- All of the Air Monitoring Stations – See Asset Map for the specific locations
- Greater Miami Convention & Visitors Bureau
- Miami-Dade County Tourist Development Council
- Pelican Harbor Seabird Station, Inc.
- Transit Alliance Miami
- Fire Rescue team
- Miami-Dade Police Department
- Water and Sewage
- Parks, Recreation and Open Spaces
- Miami Dade Ambulance
- MCT Express Ambulance Services
- AMR Miami-Dade
- Miami Youth Sports Leagues
- YMCA of South Florida
- The Miami Foundation
- Adrienne Arsht-Rockefeller Foundation Resilience Center
- Aviation (Miami International Airport)
- Regulatory and Economic Resources
- Strategic Procurement
- Transportation and Public Works
- Biscayne Bay Foundation
- American Lung Association
- The Sierra Club Miami Group
- Parks
